Cause
- Area of hematopoietic marrow that produces area of radiolucency. Can be a result of aberrant bone regeneration after tooth extraction, persistent fetal marrow, marrow hyperplasia in response to increased demand for erythrocytes.
Incidence
- 75% are adult women
Location
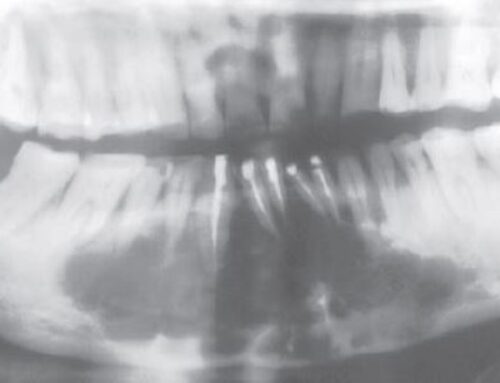
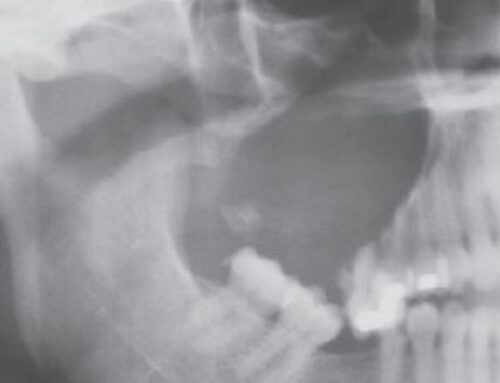
- 70% occur in posterior mandible, most often in edentulous areas
Clinical Features
- Typically asymptomatic and found incidentally on a radiographic exam
Radiographic Features
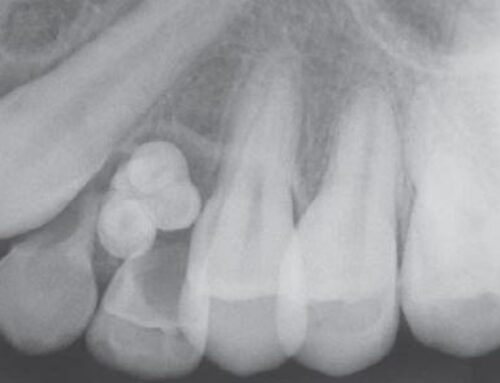
- Often well circumscribed.
- On highly detailed periapical radiographs, defect exhibit ill-defined borders and fine central trabeculations.
- No expansion of bone is noted.
Histopathology
- Cellular hematopoietic and fatty marrow.
Treatment
- Once diagnosis is established, no treatment is needed.