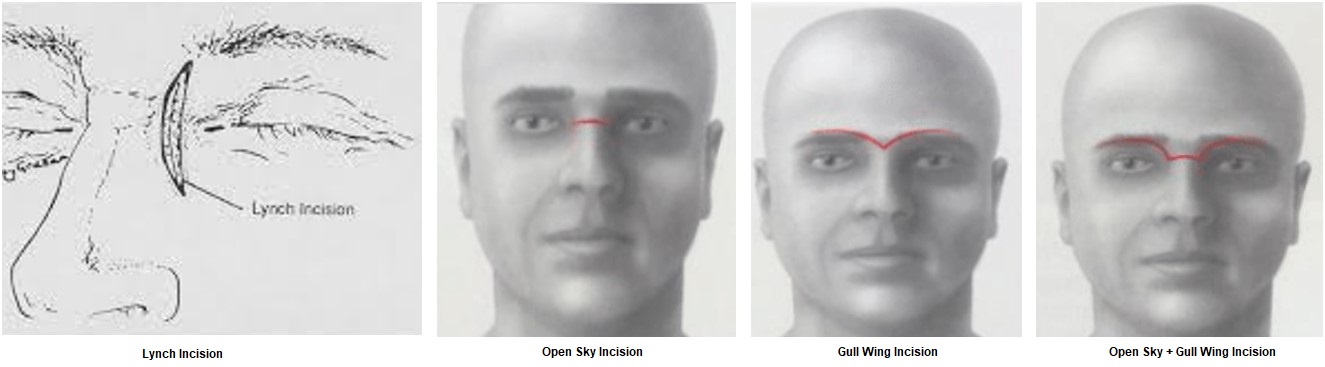
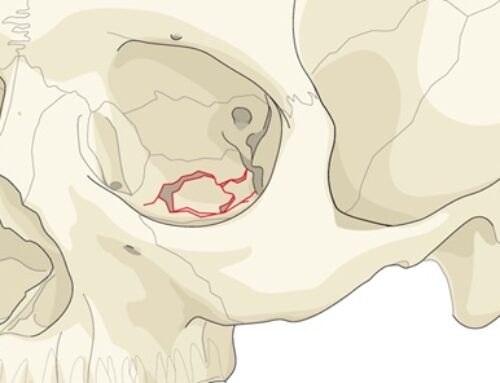
Exam & Assessment
- Same as nasal bone fracture
- Pain
- Bleeding
- Swelling
- Laceration
- Crepitation/bony step
- Mobility of the segment
- Deviation of dorsal hump/septum
- Septal hematoma
- Epiphoria
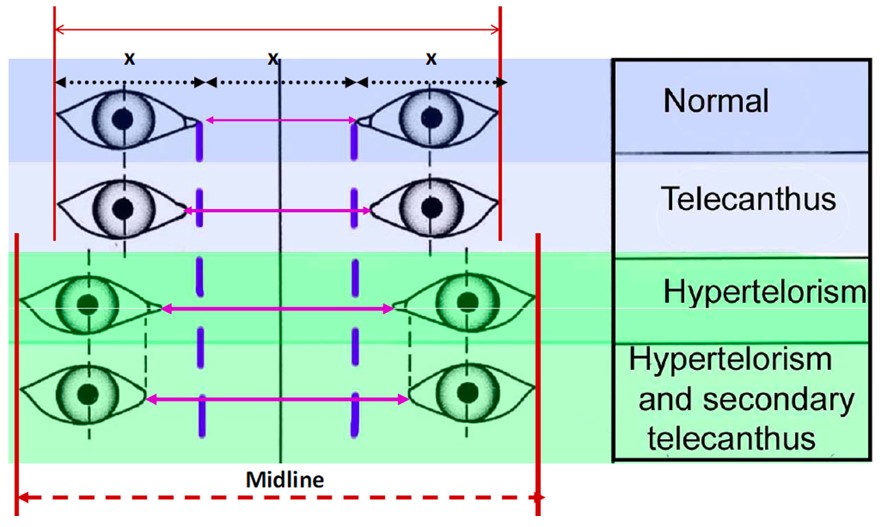
- Telecanthus
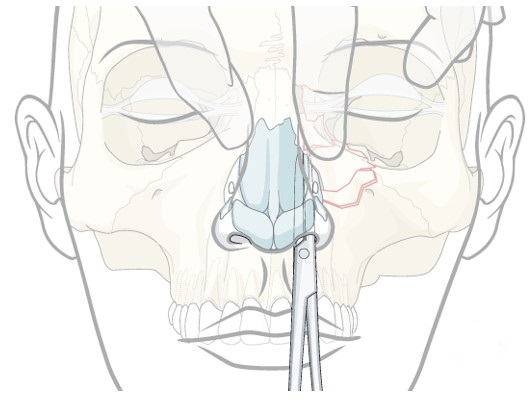
Markowitz and Manson
- Type I: single large fragment, with canthal ligament attached to lacrimal crest
- Type II: comminuted central fragment with the canthal ligament attached to a fragment of bone
- Type III: comminution with the canthal ligament detached
| Type I | Type II | Type III |
| Superior fragment stabilization at the superior medial orbital rim
Reduction and stabilization at inferior orbital rim and pyriform aperature No transnasal wiring needed |
Same as Type 1, plus:
Repositioning of the canthal-bearing bone segment May need to transnasal wiring to re-suspend medial canthus |
Same as Type II
Will need to perform canthopexy May need to bone graft |
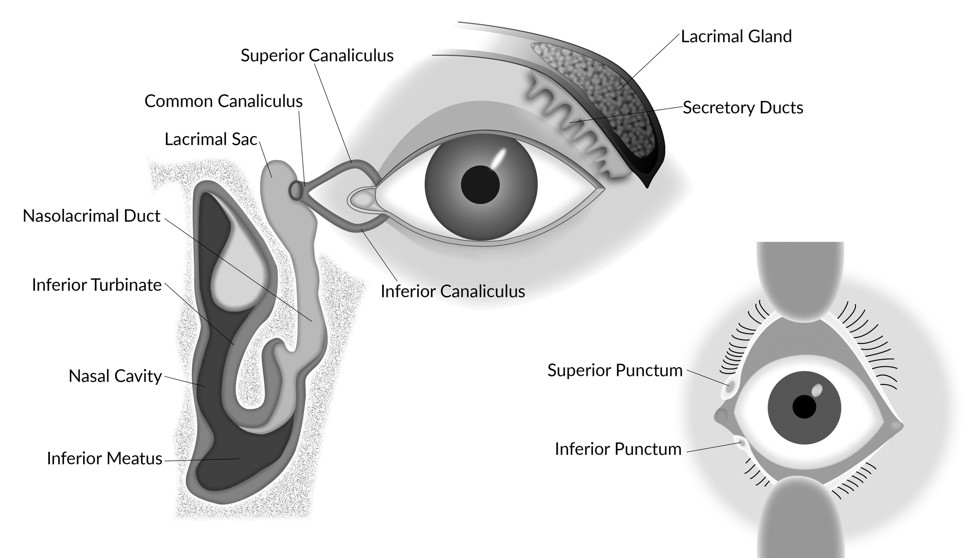
Patency Test of Lacrimal System
Jones Dye Test 2 (Secondary)
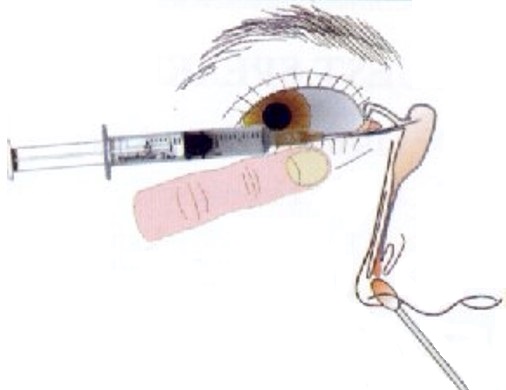
- Irrigate dye from inferior cul-de-sac. The lacrimal punctum is anesthetized and an irrigating catheter is inserted to allow thorough irrigation of the system,
- Complete obstruction: no fluid detected in nose
- Partial obstruction: dye is detected in the inferior meatus
- Upper collecting system obstruction: only clear saline
Crawford Tube
- Crawford tube placement involves cannulation of the upper and lower puncta of the lacrimal system, followed by maneuvering the metal end of the tube through the lacrimal system and out the Hasner valve to the floor of the nose.