Alcohol Withdrawal: Stages, Management, and Life-Threatening Complications
By Dr. Paul Mirdamadi
Alcohol withdrawal is a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when individuals with chronic alcohol use abruptly reduce or stop alcohol consumption. It is especially relevant in hospitalized and postoperative patients, where access to alcohol is suddenly interrupted. Early recognition, appropriate staging, and timely treatment are critical to preventing severe complications such as seizures, delirium tremens, and Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome.
Pathophysiology of Alcohol Withdrawal
Chronic alcohol use enhances GABA-mediated inhibitory tone and suppresses NMDA glutamate activity in the central nervous system. Over time, the brain compensates by downregulating GABA receptors and upregulating excitatory pathways.
When alcohol intake abruptly stops, this balance is lost, resulting in unopposed excitatory activity, which manifests as autonomic hyperactivity, neurologic symptoms, and psychiatric disturbances.
Stages of Alcohol Withdrawal
Alcohol withdrawal follows a predictable timeline, although severity varies between individuals.
Early Withdrawal (3–36 hours)
Patients develop minor symptoms similar to withdrawal from other CNS depressants. These include tremor, anxiety, insomnia, diaphoresis, nausea, and tachycardia.
Withdrawal Seizures (6–48 hours)
Generalized tonic-clonic seizures may occur, often without warning. These seizures are typically brief but may recur and indicate progression to more severe withdrawal.
Alcoholic Hallucinosis (12–48 hours)
Patients experience hallucinations—most commonly visual, but sometimes auditory or tactile—while maintaining a clear sensorium. Unlike delirium tremens, orientation is usually preserved.
Delirium Tremens (48–96 hours)
Delirium tremens (DTs) occurs in approximately 5% of patients with alcohol withdrawal and represents a medical emergency. It is associated with high morbidity and mortality if untreated.
Delirium Tremens (DTs)
Delirium tremens is a life-threatening alcohol withdrawal syndrome that typically peaks 2–4 days after the last drink.
Clinical Features
DTs are characterized by:
-
Severe autonomic hyperactivity (tachycardia, hypertension, hyperthermia)
-
Tremors and agitation
-
Confusion and fluctuating consciousness
-
Hallucinations
-
Seizures
-
Electrolyte abnormalities
-
Respiratory alkalosis
DTs classically occur in hospitalized patients—particularly 2–4 days postoperatively—who are unable to drink alcohol during admission.
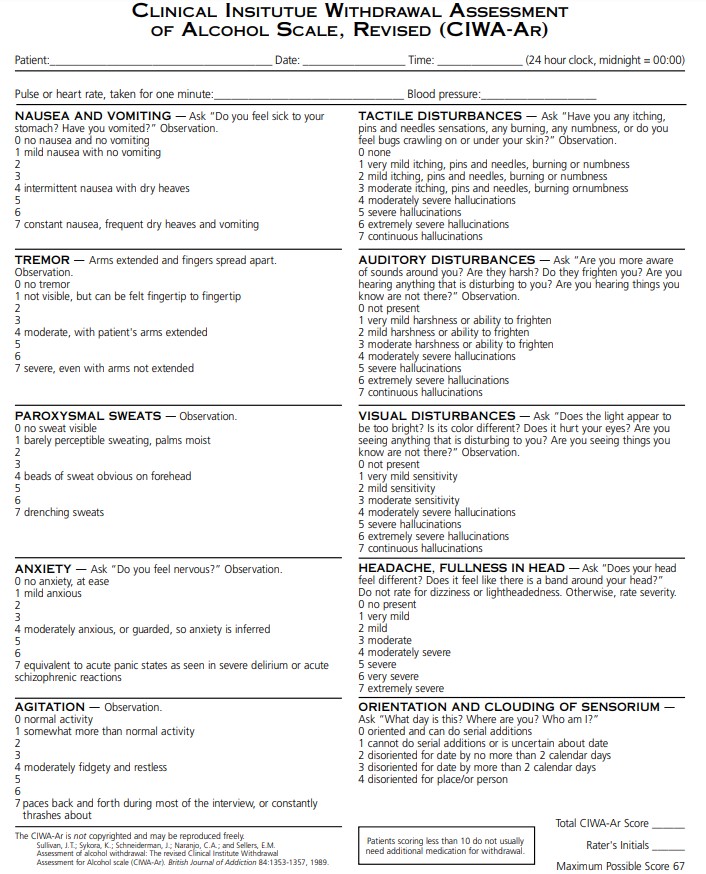
Assessment: CIWA-Ar Scale
The Clinical Institute Withdrawal Assessment of Alcohol Scale (CIWA-Ar) is the standard tool used to quantify withdrawal severity and guide treatment. It evaluates symptoms such as tremor, agitation, hallucinations, nausea, anxiety, and orientation.
CIWA-guided therapy allows for symptom-triggered benzodiazepine dosing, reducing both undertreatment and oversedation.
Treatment of Alcohol Withdrawal
First-Line Therapy: Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines are the cornerstone of treatment and act by restoring inhibitory GABA tone.
Commonly used agents include:
-
Lorazepam
-
Diazepam
-
Chlordiazepoxide
Long-acting benzodiazepines are preferred for DTs due to smoother withdrawal control and reduced seizure risk.
Adjunctive Medications
-
Morphine may be used if agitation is due to poor analgesia, not withdrawal itself.
-
Haloperidol is appropriate for isolated postoperative delirium, but it is not first-line for alcohol withdrawal and does not prevent seizures.
Haloperidol dosing:
-
IM or IV (off-label): 2–10 mg; may repeat every ≥15 minutes for acute agitation (maximum ~30 mg/day)
-
Oral: 2–10 mg every 6 hours as needed (lower doses may suffice in some patients)
Banana Bag Therapy
A banana bag is often administered to patients with chronic alcoholism to address nutritional deficiencies.
Typical Composition
-
1 liter normal saline
-
Thiamine 100 mg
-
Folic acid 1 mg
-
Multivitamin infusion (1 ampule)
-
Magnesium sulfate 3 g
The infusion is typically administered over 4–8 hours, with the yellow color derived from folic acid and multivitamins.
Updated Evidence
Recent evidence suggests that 100 mg of thiamine is inadequate for ICU patients at risk of Wernicke encephalopathy. Current recommendations support:
-
Thiamine 200–500 mg IV every 8 hours during the first 24 hours of admission
There is limited evidence supporting routine multivitamin use, and less dramatic dosing changes are recommended for magnesium and folate.
Wernicke–Korsakoff Syndrome
Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome results from vitamin B1 (thiamine) deficiency, most commonly seen in chronic alcoholics.
Wernicke Encephalopathy
Characterized by the classic triad:
-
Confusion
-
Ophthalmoplegia
-
Ataxia
Korsakoff Syndrome
Represents the chronic, irreversible phase, marked by:
-
Severe memory impairment
-
Confabulation
-
Personality changes
Importantly, administration of dextrose before thiamine can precipitate Wernicke encephalopathy by worsening thiamine depletion.
Treatment
-
Immediate IV thiamine replacement
-
Thiamine should always be given before glucose
Clinical and Board Exam Pearls
-
Alcohol withdrawal seizures occur 6–48 hours after cessation
-
Delirium tremens peaks 2–4 days after last drink
-
Benzodiazepines are first-line therapy
-
CIWA-Ar guides symptom-triggered treatment
-
Give thiamine before dextrose
-
DTs commonly occur postoperatively in hospitalized alcoholics
Conclusion
Alcohol withdrawal is a predictable but potentially fatal condition that requires early recognition and aggressive management. Understanding the stages of withdrawal, proper use of benzodiazepines, and prevention of nutritional complications such as Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome is essential for safe perioperative and inpatient care.







