Skip to content
Random Anatomy
- Serratus Anterior – ribs 1-8
- External oblique – ribs 5-12
- When access pleural cavity, pierce above external oblique
- Temporal branch of CN VII – lies immediately beneath the temporoparietal fascia above the superficial layer of the temporalis fascia.
- Lingual nerve – lies above the mandibular 3rd molar alveolar crest 14% of the time.
- Marginal mandibular nerve – is below the inferior border of mandible 19% of the time when posterior to the facial arteries
- Normal intercanthal distance: 33±2
- Nasolabial angle: male-90-95⁰, female-95-110⁰
- Upper eyelid margin to superior tarsal crease : 9-10mm
- Internal nasal valve: 10-15⁰ (junction of upper lateral cartilage and nasal septum
- Bizygomatic width: male 0.88, female 0.86
- Nasion perpendicular to A point: normal -3 to -5
- Erb’s point: 6cm inferior to the ear lobule and along the anterior sternomastoid border (avoid to prevent injury to greater auricular and accessory nerve)
- Hinderer’s Point (malar eminence): intersection of lateral canthus and labial commissure with ala and tragus
- Modiolus: confluence of five muscles of facial expression including levator anguli oris, zygomaticus major, risorius, platysma, depressor anguli oris. These muscles are bound to the buccinator by connective tissue and represent the configuration of the nasolabial fold
- McGregor’s patch “bloody gulch” – an area near the zygomatic prominence where a plexus of vessels is found
- Auriocephalic angle – 25 to 35 degree
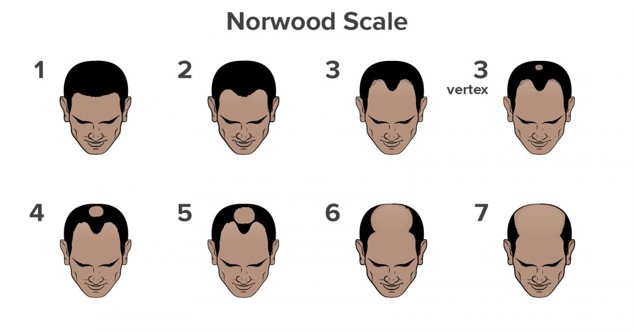
- Norwood – male pattern hair loss classification
- Apertognathia – open bite
- Alveolar fracture – arch bar for 3-4 weeks
- Nasofrontal Angle
- angle between a line connecting the nasal bridge and nasion and a line connecting nasion and glabella. Nasion is ideally located at the upper eyelid margin and 4-6mm behind glabella.
- Normal range for the nasofrontal angle is 115 to 130 degrees
- Columellar show is the amount of columella which is seen below the alar rim. This is normally in the range of 2 to 4mm. Excessive or insufficient columellar show should be addressed in esthetic rhinoplasty.
- The most ideal position of the cheek eminence is located 10mm lateral and 15-20mm inferior to the lateral canthus. This mark aids in the proper superior-inferior and lateral positioning of the cheek implant.
- Erb’s point is approximately 6 cm inferior to the lobule of the ear and along the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, where the platysma crosses it obliquely. Remaining superficial to the fascia over the sternocleidomastoid muscle in this region ensures that injury to the greater auricular and accessory nerves is avoided.
- Modiolus: The modiolus is an area of confluence of five muscles of facial expression, located lateral to the corner of the mouth. The five muscles are the levator anguli oris, zygomaticus major, risorius, platysma, and depressor anguli oris. This group of muscles is bound to the buccinator by connective tissue, and along with the cheekbone, represent the configuration ofthe nasolabial fold.
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
Page load link

